Maximizing Luxury and Minimizing Impact
Written By: James Aiken
Bigger used to be better when it came to the housing market in America. Size still matters in the housing market but the scales are tipping in favor of the smaller end. There are many reasons for the reversal of housing preferences. Younger Americans are opting for a minimalist lifestyle that offers smaller and simpler living.
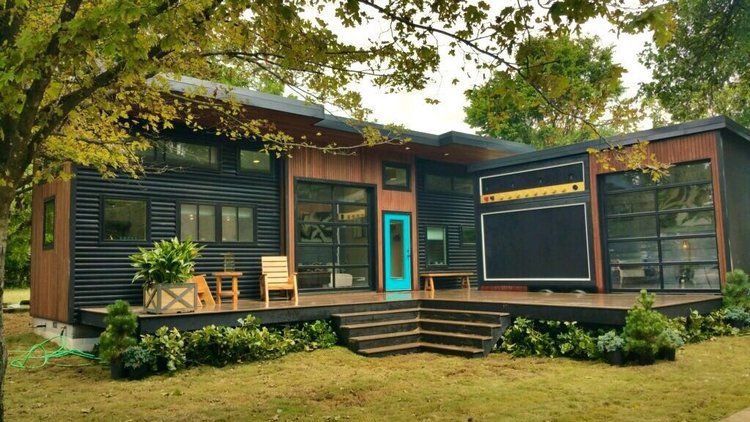
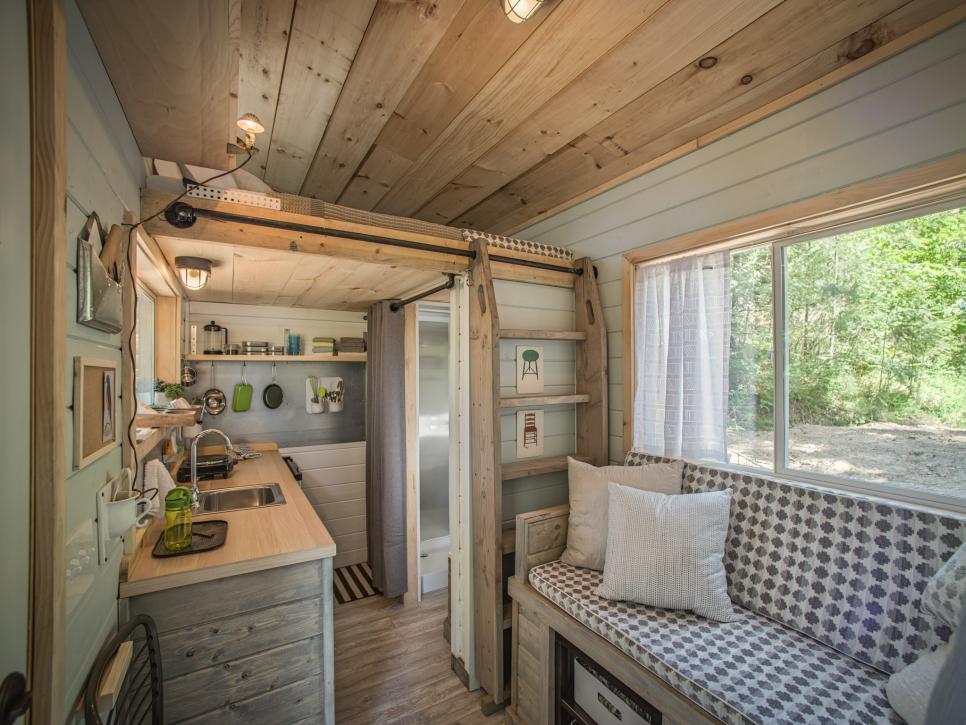
Many of the homeowners that are joining this movement are opting to live in tiny houses. These houses reduce the size of the home substantially but still offer many of the same amenities.

Smaller Homes, Bigger Wallets
Americans are choosing to follow the tiny house movement for a variety of reasons. Among the top reasons are financial concerns, environmental concerns, and freedom from huge property maintenance. The typical American spends up to 50 percent of their income on normal housing costs. This cost can be reduced drastically by building a home to be just the size that you need.
A popular trend is to use the money saved on reducing the size to provide amazing amenities to the homes. There are tiny homes as small as 300 square feet that have solar power, hot tubs ad even bars. These could be purchased due to the amount of money saved by reducing square footage.
The trend of wanting smaller homes with high-quality materials and top of the line amenities is not only in the tiny house market but in the regular home market as well. Last year the typical new home that was manufactured dropped in square footage. This was the first drop in size since 2009 which shows that this trend is rapidly catching on.
Affordable Luxury
The average millennial home buyer is looking for substance instead of size. House size is becoming less important. Many homeowners are looking for things like energy star rated appliances, smart thermostats, low energy windows, and other energy-efficient amenities. New homeowners also seem to be leaning toward patios, wrap around porches and separate laundry rooms.
Most people looking for a home prefer building a new structure as opposed to buying an existing home. This means that the homeowners can add the amenities and the square footage that they want as opposed to more expensive renovations to existing structures. These homeowners are also moving out of cities with 65% of them wanting to build their houses in the suburbs.
Most of these millennial first time homeowners would prefer to build a new house. However, most are purchasing existing homes simply because it is an easier process, they can get deals on foreclosed homes, and they can move in almost immediately.
Do It Yourself: Tiny General Contracting
These homeowners are turning to the reality television craze to learn how to add amenities and features to their homes on their own. These do it yourself home improvement shows are starting a trend of homeowners making improvements to their homes on their own.
Many of these renovations tend to be outdoor spaces for entertaining company and relaxing. Decks, fences, and vegetable gardens top the list but gazebos, swimming pools, hot tubs, and BBQ pits are up there on the top of the list as well.
The biggest thing these millennials are looking for is value. They are looking to add to the equity of these homes so they can flip them for a profit and build their own homes the way they want. After these homes sell, they are tending to build homes that are smaller and have amenities such as mud rooms, separate laundry rooms, and gathering places such as outdoor kitchens with a dining area. Millennials seem to like to gather in groups and be close-knit by having parties and cookouts.
The state of the economy forced many Americans to be frugal in spending. This is the reason the trend for building smaller homes began. New Home building companies are building smaller homes to stay in business. They knew that big extravagant homes were not going to sell in the market at the time and began to market smaller more affordable homes.
Housing Market is Bigger, but Less Affordable
Over the last thirty years’ homes have more than doubled in size for the average home. Back then the average new home was 1,700 square feet. Any homeowner who has a house that was built in the previous decade has a living area that is four times larger than most of the homes built in the 1950’s. Many of these homes are being foreclosed and sold at low prices and in turn that brings down the price of other homes on the market.
Most construction companies are reporting that their clients are asking for smaller homes and 90% of these companies stated that they are either planning to build smaller homes or are already in the process of building them.
The trend to move toward smaller cost efficient homes began before or at the beginning of the recession. The housing market started to hit rock bottom and devastated homeowners began looking at these large homes as a bad investment and realized how much of a cash drain they had on their hands. These larger homes are not only more expensive because of the building materials but they cost more to heat and cool, property taxes are higher, and maintenance is harder and costs more.

Waste Not, Want Not
Therefore, homeowners are transitioning to smaller homes. Smaller homes are more cost efficient, easier to clean, and cheaper to furnish with those high-quality amenities that everyone seems to want.
This trend can be seen in divorces of all things. Divorcing couples used to fight over who was going to get the house and all the costs associated with it because neither wanted it. Now divorcing couples are fighting to try and keep the homes for themselves.
Living in a smaller home also makes homeowners think wisely about the things they want in their home because of less space. All of this has led to homeowners using the money they saved to purchase the high-quality amenities.
Taking Advantage of the Environment
These homeowners have made the decision to go with quality over quantity and everyone benefits from this trend. Not only is this trend great for the environment but also good for the housing market and economy because fewer people are foreclosing on homes because they can afford to keep them due to the money saved by swapping square footage for nice amenities.